Watching your father, grandfather, or other family members experience hair loss can feel like previewing your inevitable future. While genetics play a significant role in male and female pattern baldness, your genetic predisposition is not an absolute sentence. Understanding how hereditary baldness works, recognizing early warning signs, and implementing natural prevention strategies can significantly slow hair loss, preserve density, and in some cases even promote regrowth. This comprehensive guide explores science-backed natural approaches to controlling baldness when it runs in your family, giving you the tools to fight your genetic tendencies and maintain healthier hair longer.
Understanding Hereditary Hair Loss
How Genetics Cause Baldness
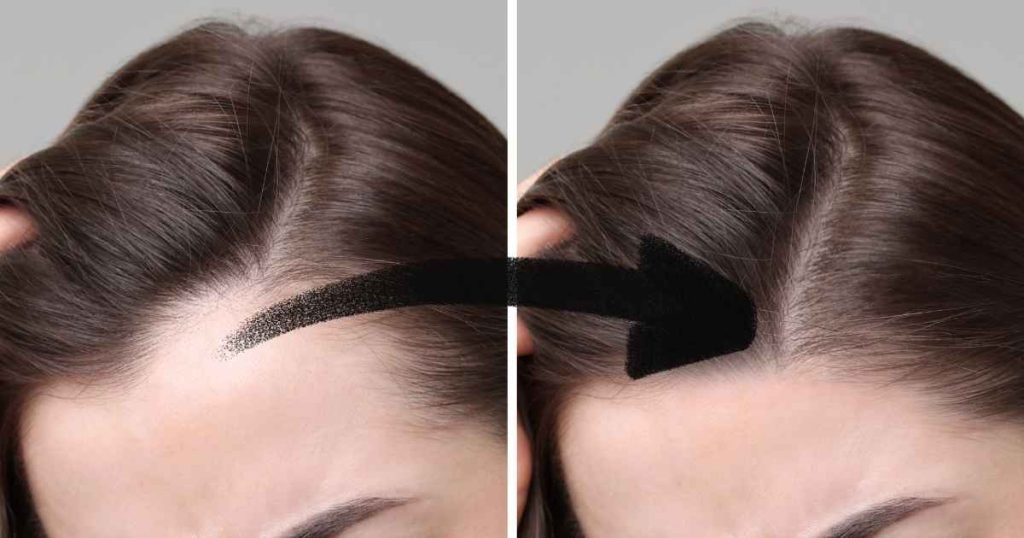
Hereditary hair loss, called androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of baldness affecting both men and women. This condition results from your genetic sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. When you inherit genes that make your hair follicles sensitive to DHT, this hormone gradually shrinks follicles, shortening their growth phase and eventually preventing them from producing visible hair.
The genetics of baldness are complex, involving multiple genes inherited from both parents. You can inherit baldness genes from your mother’s side, father’s side, or both. The common myth that baldness only comes from your mother’s father is false. If multiple family members on either side experience hair loss, your risk increases significantly. These genetic factors determine not only whether you will experience hair loss but also the pattern, severity, and age of onset.
Understanding your genetic risk does not mean accepting inevitable baldness. While you cannot change your genes, you can influence how they express themselves through lifestyle factors, nutrition, and targeted interventions. Early action provides the best outcomes, as preventing hair loss is easier than reversing significant balding.
Male vs. Female Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness typically begins with a receding hairline at the temples and crown thinning. It progresses to form an M-shape at the front and can eventually lead to complete baldness on top, leaving hair only on the sides and back. Men may notice thinning as early as their late teens or twenties, though it more commonly begins in the thirties and forties.
Female pattern baldness presents differently, usually causing overall thinning across the top of the scalp while maintaining the frontal hairline. Women rarely experience complete baldness but may develop noticeably wider parts and decreased hair density. Female hair loss typically becomes apparent in the fifties and sixties, though it can begin earlier, especially after hormonal changes like pregnancy or menopause.
Recognizing Early Warning Signs
Early detection allows you to implement prevention strategies before significant hair loss occurs. Watch for increased hair shedding beyond the normal 50-100 hairs daily. Notice if more hair collects in your shower drain, on your pillow, or comes out when you run your fingers through your hair. Pay attention to changes in hair texture, as thinning hair often becomes finer and less robust before falling out.
For men, check your hairline regularly by comparing photos taken months apart. Look for temple recession or M-shape formation. Monitor your crown by taking overhead photos with consistent lighting. For women, notice if your part appears wider or if you can see more scalp through your hair. Check if ponytails feel thinner or if you need to wrap hair ties more times.
The earlier you address hair loss, the better your results. Hair follicles that have been dormant for years become increasingly difficult to reactivate. Acting when you first notice changes gives you the best chance of preserving and maintaining your hair density.
Dietary Changes to Support Hair Health
Protein: The Foundation of Hair Growth
Hair is made primarily of keratin, a protein. Inadequate protein intake directly impairs hair growth and quality. Your body prioritizes protein for essential functions, so hair gets what is leftover. When protein is insufficient, your body shifts hair follicles into resting phase, causing increased shedding months later.
Aim for at least 0.8-1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight daily, more if you exercise regularly. Excellent protein sources include eggs, fish, chicken, turkey, lean beef, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, legumes, and protein powder. Distribute protein across meals rather than consuming most at dinner. Include protein at breakfast to provide amino acids for hair follicle repair and growth throughout the day.
Iron for Healthy Hair Follicles
Iron deficiency is a common yet overlooked cause of hair loss, particularly in women. Iron delivers oxygen to hair follicles, supporting their high metabolic demands. Low iron reduces follicle function even before causing anemia. Many people with hair loss have suboptimal iron levels within normal range but below optimal for hair growth.
Include iron-rich foods like red meat, organ meats, sardines, spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals. Animal sources provide heme iron that absorbs better than plant-based non-heme iron. Vitamin C enhances iron absorption, so combine iron foods with citrus fruits, bell peppers, or tomatoes. Avoid consuming iron with calcium, tea, or coffee which inhibit absorption. If you suspect iron deficiency, request blood tests for ferritin, which measures iron stores.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Scalp Health
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation that can damage hair follicles and impair growth. These essential fats also support scalp health, providing the environment hair needs to thrive. Studies show omega-3 supplementation can increase hair density and reduce hair loss in people with thinning hair.
Eat fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and herring at least twice weekly. Plant sources include walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds. Consider fish oil or algae-based omega-3 supplements if you do not eat fish regularly. Look for supplements providing at least 1,000-2,000 mg combined EPA and DHA daily.
Vitamins and Minerals That Support Hair
B vitamins, particularly biotin and B12, support hair growth and may reduce shedding. Vitamin D deficiency associates with hair loss, and supplementation may help when levels are low. Vitamin E provides antioxidant protection to hair follicles. Vitamin A supports sebum production that keeps scalp and hair healthy.
Zinc deficiency causes hair loss, but excessive zinc can also cause problems, so balance matters. Selenium supports thyroid function, which influences hair growth. These nutrients work synergistically, so focus on a varied, nutrient-dense diet rather than mega-dosing individual nutrients. Eat colorful vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and quality proteins to cover all nutritional bases.
Essential Supplements for Hereditary Hair Loss
Saw Palmetto: Natural DHT Blocker
Saw palmetto extract may help prevent hair loss by blocking the enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT. While research shows mixed results, some studies find saw palmetto reduces hair loss and promotes regrowth in men with androgenetic alopecia. It appears less effective than prescription medications but offers a natural alternative with fewer side effects.
Typical doses range from 320 mg daily of standardized extract. Saw palmetto is generally safe but may cause mild digestive upset. It can interact with hormone medications and blood thinners. Give saw palmetto at least 3-6 months to show effects. Do not expect dramatic results, but it may slow hair loss progression when combined with other approaches.
Biotin for Hair Strength
Biotin, a B vitamin, supports hair structure and growth. True biotin deficiency is rare but can cause hair loss. Supplementation helps when deficient but may not benefit those with adequate levels. Despite limited evidence for treating genetic hair loss, many people report subjectively improved hair quality with biotin supplementation.
Common doses range from 2,500-10,000 mcg daily. Biotin is water-soluble with low toxicity risk. However, high doses can interfere with certain lab tests including thyroid function tests. Inform your doctor if you take biotin supplements before blood work. Food sources include eggs, nuts, seeds, salmon, and sweet potatoes.
Marine Collagen Peptides
Collagen supplements may improve hair growth, thickness, and overall quality. Collagen provides amino acids that form keratin, the protein in hair. Some research suggests collagen peptides increase hair shaft diameter and reduce hair loss. The evidence remains limited but promising.
Look for hydrolyzed marine collagen peptides which absorb well. Typical doses range from 5-10 grams daily. Mix collagen powder into smoothies, coffee, or other beverages. Collagen is very safe with minimal side effects. Give it at least 3-6 months for noticeable hair improvements.
Vitamin D Supplementation
Vitamin D receptors exist in hair follicles, and deficiency associates with hair loss. Supplementing vitamin D when deficient may help reduce shedding and support regrowth. However, benefits appear limited to those with low levels. Test your vitamin D before supplementing to determine if you need it.
If deficient, take 1,000-2,000 IU of vitamin D3 daily, adjusting based on blood levels and doctor recommendations. Vitamin D is fat-soluble, so take it with meals containing fat for better absorption. Retest levels after 2-3 months to ensure you have reached adequate levels. Excessive vitamin D can cause toxicity, so do not mega-dose without medical supervision.
Scalp Care and Massage Techniques
Benefits of Scalp Massage
Regular scalp massage increases blood flow to hair follicles, delivering more nutrients and oxygen. One study found daily 4-minute scalp massages for 24 weeks increased hair thickness. Massage may also reduce stress, which contributes to hair loss. While effects are modest, scalp massage is free, safe, and feels good.
Use your fingertips to apply gentle pressure and circular motions across your entire scalp. Spend 5-10 minutes daily massaging while watching TV or before bed. Use no products or add natural oils like coconut or rosemary oil for enhanced benefits. Be gentle to avoid pulling or damaging hair. Consistency matters more than intensity.
Proper Hair Washing Techniques
Wash hair with lukewarm rather than hot water, which can dry scalp and damage hair. Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos that do not strip natural oils excessively. Focus shampoo on the scalp where oil and buildup accumulate rather than the hair shaft. Rinse thoroughly to prevent product buildup that can clog follicles.
Condition only the ends of your hair, avoiding the scalp which can become greasy. Pat hair gently with a towel rather than rubbing vigorously. Avoid harsh brushing when wet, as hair is most vulnerable to breakage. Use wide-tooth combs to detangle gently. Let hair air dry when possible to minimize heat damage.
Avoiding Damaging Styling Practices
Minimize heat styling tools including blow dryers, flat irons, and curling irons which damage hair structure over time. When you must use heat, apply heat protectant products and use the lowest effective temperature. Avoid tight hairstyles like ponytails, braids, or buns that pull on hair follicles, causing traction alopecia.
Chemical treatments including bleaching, perming, and relaxing weaken hair and can damage follicles. Minimize or eliminate these treatments if you are prone to hair loss. Skip harsh hair products with alcohol or strong chemicals. Choose gentle, natural products whenever possible. Treat your hair delicately, as genetic hair loss makes each strand more precious.
Natural Topical Treatments
Rosemary Oil for Hair Growth
Rosemary essential oil shows promise for treating hair loss. One study found rosemary oil as effective as minoxidil for promoting hair growth after six months of use. Rosemary oil may improve circulation, have anti-inflammatory properties, and promote nerve growth that supports follicle function.
Mix 5-10 drops of rosemary essential oil with a tablespoon of carrier oil like coconut, jojoba, or olive oil. Massage into your scalp and leave for at least 30 minutes before washing out. For best results, apply 2-3 times weekly. Some people leave it overnight. Never apply undiluted essential oil directly to your scalp, as it can cause irritation.
Pumpkin Seed Oil
Pumpkin seed oil may block DHT similarly to saw palmetto. A small study found men taking pumpkin seed oil supplements experienced 40 percent more hair growth than placebo group. Whether topical application provides similar benefits remains unclear, but anecdotal evidence suggests it may help.
Apply pumpkin seed oil directly to scalp or take 400 mg supplements daily. Food-grade pumpkin seed oil can be used as a carrier oil for other essential oils in scalp treatments. Include pumpkin seeds in your diet for additional benefits. Combine approaches for potentially enhanced effects.
Onion Juice for Follicle Stimulation
Onion juice applied to the scalp may promote hair growth. Studies show onion juice increases growth factors and improves blood flow to follicles. One study found 87 percent of participants using onion juice experienced regrowth after six weeks. While the smell is unpleasant, results may be worth tolerating.
Blend or grate onions, strain to extract juice, and apply to scalp. Leave for 15-30 minutes before washing thoroughly. Use 2-3 times weekly. The sulfur compounds in onions may stimulate collagen production and improve circulation. Some people mix onion juice with honey or coconut oil to make it more pleasant.
Green Tea Rinse
Green tea contains EGCG which may inhibit DHT production and promote hair growth. While evidence is limited, green tea’s antioxidants may protect follicles from damage. Green tea rinses are safe and may provide modest benefits alongside other treatments.
Brew strong green tea, let it cool completely, and use as a final rinse after shampooing. Massage into scalp and leave for 10 minutes before rinsing with water. Alternatively, soak green tea bags in warm water and apply them directly to problem areas. Use 2-3 times weekly. Drinking green tea regularly may provide additional benefits through internal antioxidant effects.
Lifestyle Factors That Affect Hair Loss
Stress Management for Hair Health
Chronic stress accelerates hair loss through multiple mechanisms. Stress hormones push hair follicles into resting phase prematurely, causing increased shedding months later. Stress also increases inflammation and may worsen DHT sensitivity. Managing stress is crucial for controlling hereditary hair loss.
Practice daily stress reduction through meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation. Even 10-15 minutes daily reduces cortisol levels. Regular exercise is one of the most effective stress reducers while providing additional hair benefits through improved circulation. Ensure adequate leisure time and pursue hobbies you enjoy. Chronic overwork and lack of downtime significantly impact hair health.
Sleep Quality and Hair Growth
Sleep is when your body repairs and regenerates, including hair follicles. Poor sleep disrupts hormone balance, increases stress hormones, and impairs growth hormone secretion that supports hair growth. Studies link sleep disorders with increased hair loss.
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly. Maintain consistent sleep and wake times even on weekends. Create a dark, cool, quiet sleeping environment. Avoid screens for an hour before bed. Limit caffeine after 2 PM and alcohol in the evening. If you have persistent insomnia or sleep apnea, seek medical treatment as these conditions significantly affect hair health.
Exercise and Circulation
Regular exercise improves circulation throughout your body including to your scalp, delivering more nutrients and oxygen to hair follicles. Exercise also reduces stress, balances hormones, and may help regulate DHT levels. Physical activity supports overall health, which reflects in hair quality.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Include both cardiovascular exercise and strength training. Activities that increase blood flow like running, cycling, or swimming particularly benefit scalp circulation. Consistency matters more than intensity. Even regular walking provides benefits for hair health.
Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol
Smoking dramatically accelerates hair loss by reducing blood flow to follicles, increasing oxidative stress, and causing DNA damage. Studies show smokers experience earlier and more severe baldness than non-smokers. If you smoke and want to preserve your hair, quitting is one of the most impactful changes you can make.
Excessive alcohol consumption depletes nutrients needed for hair growth, particularly B vitamins and zinc. It also increases stress on your liver, which processes hormones including those affecting hair. Moderate alcohol intake, limiting drinking to a few drinks weekly, avoids these negative effects on hair health.
Understanding Realistic Expectations
Natural approaches to hereditary baldness work best for prevention and slowing progression rather than reversing advanced balding. Starting early when you first notice thinning provides the best outcomes. Hair follicles that have been dormant for years are difficult to reactivate with natural methods alone.
Expect modest results rather than dramatic transformations. Natural treatments may slow hair loss, maintain current density, or produce some regrowth in recently thinned areas. Results take months to become apparent, typically requiring 6-12 months of consistent effort. Patience and persistence are essential, as giving up after a few weeks prevents you from seeing potential benefits.
Natural methods work best when combined. Using multiple approaches that address different aspects of hair loss provides better results than relying on single interventions. Think of natural baldness control as a comprehensive lifestyle rather than quick fixes. Your overall health improvements will benefit far more than just your hair.
Monitoring Your Progress
Track your progress objectively through regular photos taken in consistent lighting from multiple angles. Take front, side, and overhead photos monthly. These visual records reveal changes that daily mirrors cannot show. Compare photos from 3-6 months apart to assess whether your interventions are working.
Monitor daily hair shedding by counting hairs that fall out in the shower and while brushing. While normal shedding ranges from 50-100 hairs daily, tracking trends reveals whether shedding is increasing, decreasing, or staying stable. Take note of hair texture and thickness changes in addition to quantity.
Be honest about what is working and what is not. If you see no improvement after 6-9 months of consistent natural approaches, consider consulting a dermatologist about medical treatments. Natural methods may not be sufficient for everyone, particularly those with aggressive hair loss. Combining natural approaches with medical treatments often provides the best outcomes.
When to Consider Medical Treatments
If natural methods are not providing adequate results after 6-12 months, or if you are experiencing rapid hair loss, consult a dermatologist. Medical treatments including minoxidil and finasteride are significantly more effective than natural approaches for androgenetic alopecia. These medications have more side effects but work for most people when used consistently.
You can combine natural approaches with medical treatments for potentially enhanced results. Natural methods support overall scalp health and may reduce medication doses needed. Discuss with your dermatologist how to integrate natural strategies with medical therapies. Some people use medical treatments to stabilize hair loss while natural methods support overall hair quality.
Advanced hair loss may require hair transplant surgery for restoration. Modern techniques produce natural-looking results with permanent outcomes. However, transplants move existing hair rather than creating new follicles. You still need ongoing treatment to prevent loss of non-transplanted hair. View transplants as part of comprehensive hair loss management rather than standalone solutions.
Final Thoughts
Controlling baldness naturally when you have family history requires dedication, patience, and realistic expectations. While you cannot change your genetics, you can influence how they express through comprehensive lifestyle approaches addressing nutrition, supplementation, scalp care, stress management, and hair-friendly practices. The strategies outlined in this guide work best when started early and maintained consistently.
Focus on protein-rich diets, essential nutrients like iron and omega-3s, evidence-based supplements including saw palmetto and biotin, gentle hair care practices, natural topical treatments, stress reduction, quality sleep, and regular exercise. These approaches work synergistically to create the optimal environment for maintaining hair density and slowing genetic hair loss.
Remember that results take time and vary individually. Some people respond excellently to natural approaches while others may need medical interventions for satisfactory outcomes. Track your progress objectively and adjust strategies based on results. Most importantly, do not let hair loss define your self-worth. Your value as a person is not determined by your hair density. These natural approaches help you fight your genetic tendencies and maintain healthier hair longer, but ultimately, confidence comes from within regardless of your hairline.